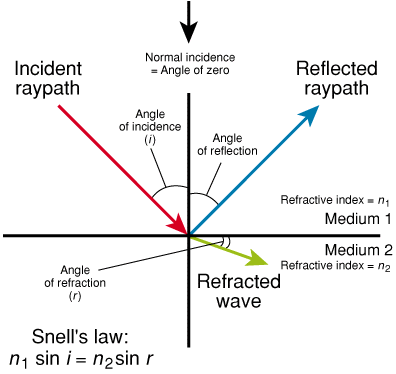
1. n. [Geophysics]
The acute angle at which a raypath impinges upon a line normal to an interface, such as a seismic wave impinging upon strata. Normal incidence is the case in which the angle of incidence is zero, the wavefront is parallel to the surface and its raypath is perpendicular, or normal, to the interface. Snell's law describes the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction of a wave.
See related terms: angle of approach, critical reflection, head wave, raypath, refraction, refractive index, refractor, Zoeppritz equations